Using jupyter on Slurm
Using Jupyter Lab on Slurm Cluster
Step 1: Start an Interactive Job on the Head Node
First, you need to request resources on the Slurm cluster. Run the following command to start an interactive job on the appropriate partition (<partition-name>) and with your account (<account-name>):
srun -p <partition-name> -A <account-name> --pty bash
Replace:
<partition-name> with your Slurm partition name (e.g., power-general). <account-name> with your Slurm account name (e.g., power-leahfa-users).
This command will allocate resources for your job and provide you with an interactive shell on a compute node (e.g., compute-0-62).
Step 2: Load the Jupyter Environment
Once inside the interactive session, load the mamba-env158/jupyter module:
module load mamba-env158/jupyter
This will prepare the environment to run Jupyter.
Step 3: Start Jupyter Lab
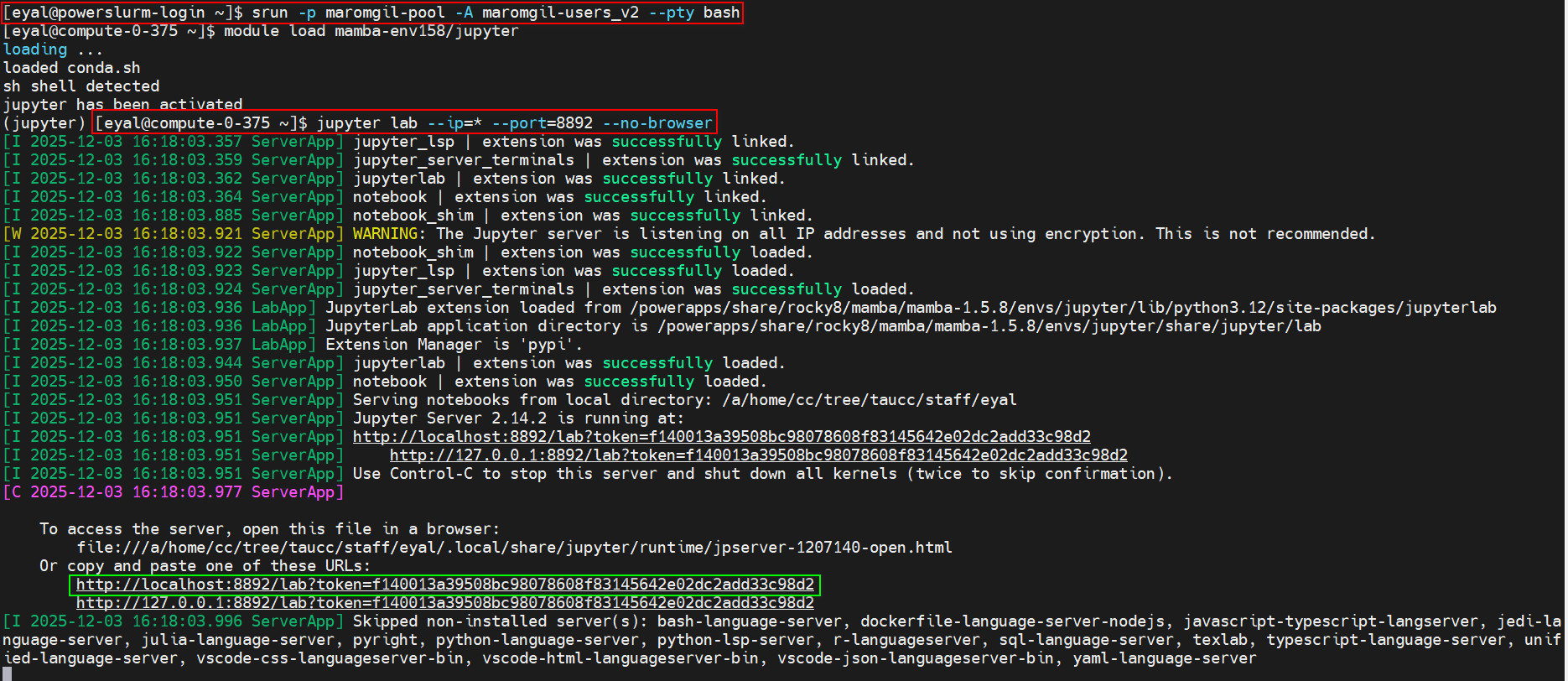
Now, start the Jupyter Lab server. Run the following command inside the interactive session:
jupyter lab --ip=* --port=8892 --no-browser
The --ip=* option binds Jupyter Lab to all available network interfaces. The --port=8892 specifies that Jupyter Lab will use port 8892. The --no-browser option prevents Jupyter Lab from opening a browser automatically.
Once Jupyter Lab starts, you should see output like this:
[I 2025-03-16 09:25:06.190 ServerApp] Jupyter Server 2.14.2 is running at:
[I 2025-03-16 09:25:06.190 ServerApp] http://localhost:8892/lab?token=<token>
Example:
Step 4: Set Up SSH Port Forwarding
To access the Jupyter Lab server from your local machine, you need to set up SSH port forwarding.
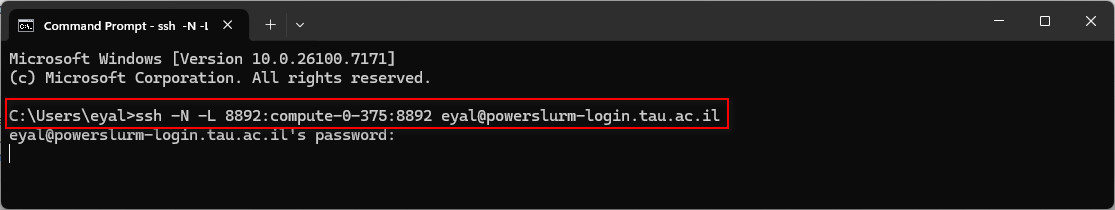
Open a terminal on your local (cmd on windows) machine and run the following command:
ssh -N -L 8892:<compute-node-name>:8892 <username>@<headnode-name>
Replace:
<compute-node-name> with the name of the compute node where Jupyter Lab is running (e.g., compute-0-62). <username> with your Slurm username. <headnode-name> with the hostname or IP address of the Slurm head node (e.g., powerslurm-login.tau.ac.il).
This command forwards port 8892 from the compute node back to your local machine.
Example:
Step 5: Open Jupyter Lab in Your Browser
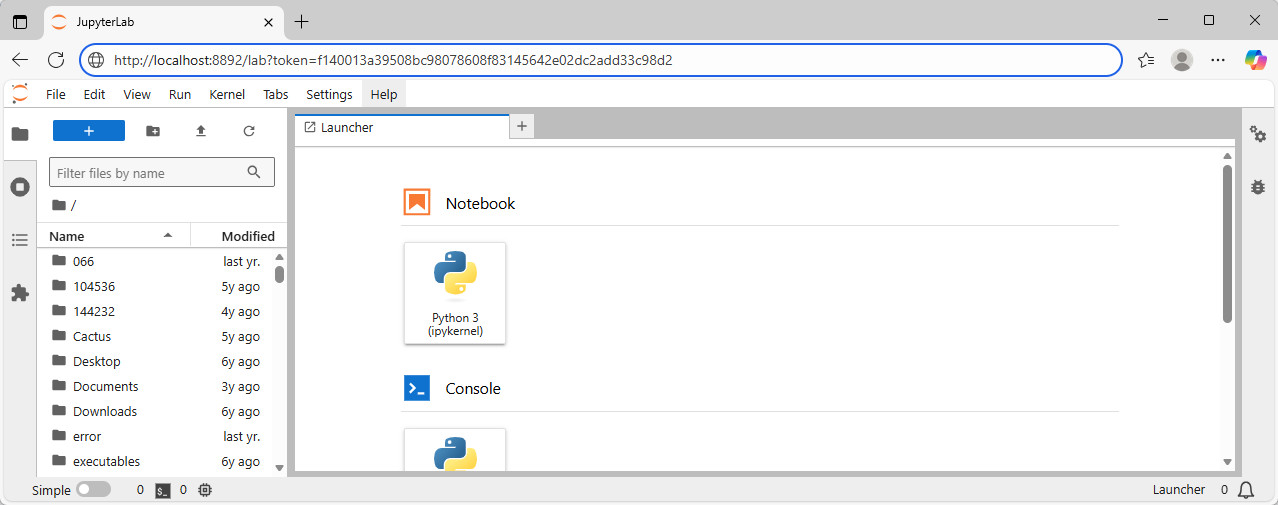
After establishing the SSH tunnel, open your web browser and navigate to:
http://localhost:8892/lab?token=<token>
This URL will give you access to your Jupyter Lab instance.
Example:
Step 6: Start Using Jupyter Lab
Once you’ve entered the token, you can start working with Jupyter Lab on your browser, using the resources of the cluster.
Step 7: Closing the Job
When you're finished using Jupyter Lab, return to the interactive session and press Ctrl+C to stop the Jupyter Lab server. Then, exit the interactive session by typing:
exit
Additional Notes:
Ensure that the SSH tunnel (ssh -N -L ...) remains open while you are working with Jupyter Lab.
You can use different ports if 8892 is already in use, just adjust the port number in both the jupyter lab command and the SSH command.
If you encounter any issues with port forwarding, double-check the node name (<compute-node-name>) and the port number.